How Long Does It Take to Recover from a Shoulder Muscle Tear?
Shoulder muscle tears and torn tendon injuries can be debilitating injuries that often lead to weeks or even months of recovery time.
Shoulder injuries are most commonly associated with damage to the rotator cuff, a group of muscles which is responsible for stabilizing the shoulder joint and allowing for an array of arm movements.
Given the intricate nature of the shoulder joint, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention if a shoulder muscle tear is suspected. Proper diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce shoulder muscle tear recovery time and help athletes return to their sport or individuals who want to regain strength and mobility in their shoulders.
In this blog post, we will discuss and examine the recovery times of shoulder muscle tears and physical therapy strategies for the most complete recovery and efficient return to daily routine and physical activities.
Anatomy of shoulder muscles
The shoulder muscles are a fascinating group of muscles that perform an incredibly complex range of movements, which is why they are often prone to injury. These muscles include the deltoid, rotator cuff, scapula stabilizers, and pectoralis major, all of which work in tandem to facilitate smooth shoulder movement.
The rotator cuff muscles, for instance, aid in overhead reaching and lifting.
The deltoid muscles of the shoulder play a crucial role in arm movement. They are responsible for helping you lift your arms overhead, move your arm, and push objects away from your body.
Deltoid muscles are located on the uppermost part of the arm, essentially forming a protective sheath around the shoulder joint.
The deltoid can be divided into three distinct sections – anterior, medial, and posterior. While each plays a significant role in shoulder movement and stability, injuries to these muscles can result in a variety of symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to debilitating pain.
Overview of shoulder muscle tears
The shoulder is remarkably versatile, having the greatest range of motion of any joint in the body. Unfortunately, this also means it can be especially prone to injury and other joint issues.
Shoulder muscle tears can vary in severity. Small tears tend to heal on their own, but a complete tear will often require surgery. Shoulder muscle injuries require immediate medical attention to prevent further damage and lessen the probability of future injuries .
For a minor shoulder sprain or mild rotator cuff injuries, a conservative treatment protocol is appropriate and involves physical therapy, rest, and avoiding activities that aggravate the injury. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair severe sprains or complete tears.
The recovery time for rotator cuff tears largely depends on the extent of the injury and the age and overall health of the individual.
While recovery times vary, it’s important to allow full recovery before returning to activities to prevent re-injury.
Risk factors for shoulder muscle injuries

Shoulder muscle tears are a common injury, especially among individuals who participate in high-impacted sports such as football. Individuals who engage in repetitive heavy lifting or overhead activities, such as weightlifters, baseball pitchers, or swimmers, are also at a higher risk of developing shoulder muscle tears.
Work-related
Shoulder injuries are not only a problem for athletes; they can also affect those in professions that involve frequent use of the shoulder, such as painting, yard care, and construction. These individuals have an increased likelihood of suffering from shoulder-related ailments.
Aging
Muscles and tendons become less elastic as they age, making them more susceptible to injury (degenerative tear). Likewise, when muscles are not properly warmed up, they become more vulnerable during physical activity. Scar tissue from previous shoulder injuries can also weaken the muscles and make them prone to new tears.
Gender
Women have a higher risk of shoulder injuries due to anatomical differences in their shoulder structure.
Anatomy
Individuals with poor posture that puts excessive stress on the shoulder muscles may eventually experience a tear. Anatomical abnormalities can contribute to shoulder problems and the likelihood of a shoulder muscle tear.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Shoulder Muscle Tears

As one of the most complex joints in the body, the shoulder is especially susceptible to muscle tears. Shoulder muscle tears are common injuries among professional athletes and laborers who engage in repetitive overhead motions, but they can also occur due to trauma or degenerative conditions.
Symptoms may include severe pain in the affected area, weakness or difficulty moving the arm, and a popping or grinding sensation felt in the shoulder socket.
An orthopedic specialist should be consulted if a muscle tear is suspected. During an examination, the physician will conduct several common orthopedic tests of the injured muscle and surrounding muscles. Additionally, imaging tests such as MRIs or ultrasound are usually used in the diagnostic process.
If additional imaging is needed, an MR arthrogram is usually ordered. This type of MRI is distinct from a regular MRI, as contrast dye is injected into the affected area. The added fluid enhances the images, making it easier to identify tears that may not have been visible before.
Types of shoulder muscle tears
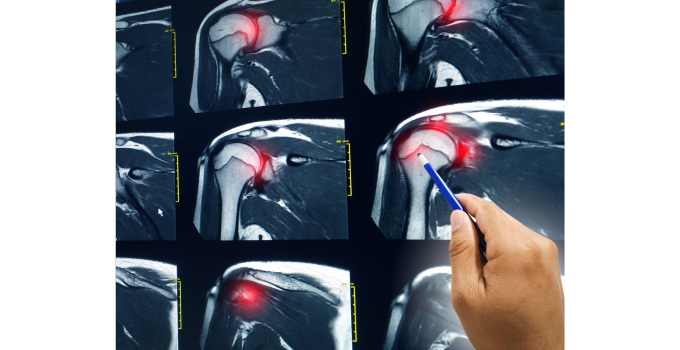
Most shoulder muscle tears consist of either rotator cuff tears or LHB tears.
Rotator cuff tear
By far the most common of shoulder muscle injuries is a torn rotator cuff. A rotator cuff tear occurs when the one or more of the muscles and tendons that cover the upper arm bone of the affected shoulder (humerus) are damaged or torn.
The rotator cuff is a complex group of four muscles including the praspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. The muscles originate at the scapula (or shoulder blade) and join as tendons to form a dense covering at the top of the humerus. The rotator cuff is responsible for stabilizing the shoulder, allowing for the full range of motion necessary for daily activities, such as lifting and rotating the arm.
The rotator cuff can become injured through overuse, age, or trauma. Athletes who engage in repetitive overhead motions like throwing or serving are particularly prone to rotator cuff tears. A rotator cuff injury can result in significant shoulder pain, weakness, and loss of motion.
LHB tears
The long head of biceps tendon (LHB) tear is an important part of the shoulder joint. This tendon originates from the shoulder blade and travels through the shoulder joint and attaches to the top of the humerus bone. It functions as a stabilizer of the shoulder joint during arm movement.
A tear of the LHB tendon involves a partial tear or a complete rupture of the tendon fibers that attach the biceps muscle to the shoulder. This can lead to considerable pain, weakness, shoulder instability, and limited range of motion. These tears can occur in a variety of ways, including sudden trauma or overuse, and they can happen to anyone, irrespective of age or activity level. Surgical intervention may be required for severe tears of the LHB tendon.
Treatment options for shoulder muscle tears

Shoulder muscle and tendon tears are painful, debilitating injuries that require careful consideration of treatment options for successful recovery. The most common and effective method for treating a milder injury like a shoulder sprain is a combination of conservative treatments like rest, compression, ice therapy, physical therapy, and pain management.
Conservative treatment
Rest is crucial, as it allows a torn rotator cuff to eventually heal and prevents further damage from occurring. Ice pack therapy can help reduce swelling and may help ease pain. Physical therapy strengthening exercises can help to strengthen shoulder muscles and improve range of motion. Pain medication may also be prescribed by a physician for pain relief during the four to six weeks healing period of a shoulder injury.
Other treatment options
In recent years, improvements in treatment options for mild shoulder muscle injuries have become available to medical professionals. Among these are improving posture and shoulder biomechanics, nerve block and steroid injections, and platelet injections. The latest research suggests that improving posture and shoulder biomechanics aid in the healing process, alleviate mild shoulder pain, may help prevent future injury to the rotator cuff, and improve overall shoulder function. Corticosteroid injections work by reducing inflammation and promoting healing. Alternatively, platelet injections can also be utilized to stimulate tissue repair and regeneration.
It is essential to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions and attend all recommended physical therapy sessions to achieve the best possible outcome. With proper care and treatment, most individuals will fully recover from a shoulder muscle injury such as a mild rotator cuff tear and eventually return to playing sports and performing daily activities without complications.
Surgery
Severe rotator cuff tears often require surgical intervention.
It is important to choose an orthopedic surgeon with expertise in repairing rotator cuff tears, ideally one who has completed a fellowship in sports medicine.
How long does it take to recover from rotator cuff surgery?
The recovery process from shoulder surgery can be a long and grueling process. The length of recovery time after rotator cuff surgery varies based on numerous factors, including the extent of the tear, the type of surgical technique, and the patient’s overall health. Generally, patients can expect to take six to eight weeks, or even several months to recover fully from surgery, with the first few weeks being the most challenging. Pain management, physical therapy, and strict adherence to activity restrictions are all critical components of a successful recovery. However, following these guidelines will lead to a full recovery and restoration of functionality.
Conclusion
A shoulder muscle injury can have significant consequences on future shoulder function and should be taken seriously.
The muscles of the rotator cuff plays a crucial role in shoulder function, as it stabilizes the joint and allows for a range of movements. Therefore, any injury to the rotator cuff can greatly impact the shoulder’s ability to function properly.
It’s important to seek further medical assistance if you experience persistent pain, weakness, or difficulty moving your shoulder, as these symptoms may indicate a rotator cuff tear. Early diagnosis and treatment of sprained shoulder injuries such as rotator cuff tears can prevent further damage and ensure a complete recovery. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to restore full function to the shoulder. Therefore, it’s essential to pay attention to any symptoms that may indicate a shoulder muscle injury and seek medical attention promptly.